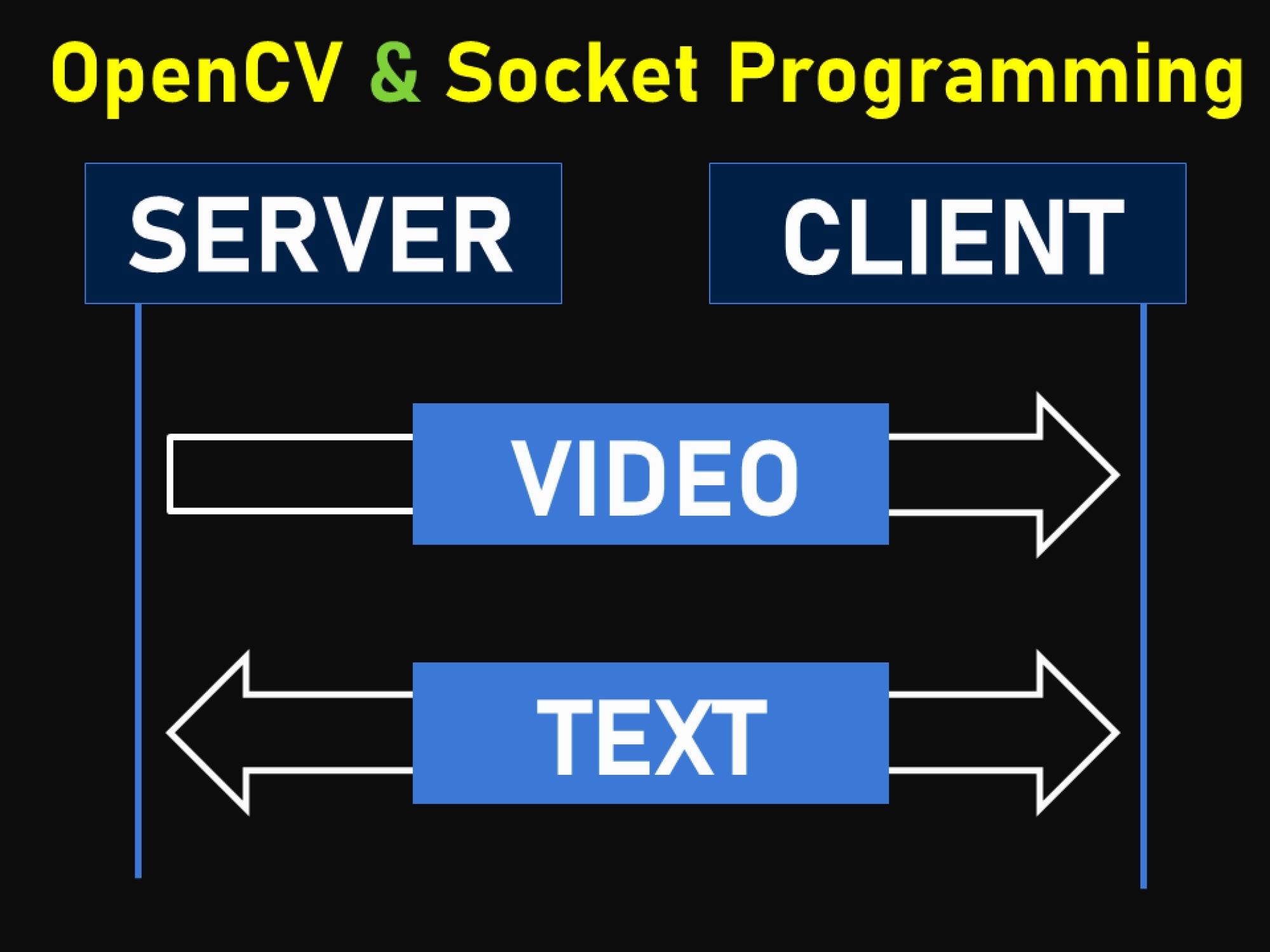
Hello friends! Today’s tutorial is about sending audio and video streams from a server to a client. These streams will be extracted from an MP4 file. We will use UDP socket for the transfer of video stream and TCP socket for the audio stream. Each MP4 file consists of these streams, with a different frame rate and audio sampling rate. Normally, the audio sampling rate is set to 44100 Hz. However, the video frame rates can vary e.g. 15 frames per second (fps), 20 fps, 24 fps, 30 fps or even more. If we simply use opencv to extract the frames of MP4 and send it (with a delay of 1 ms showing each) then it may possible that your video won’t be playing at its inherent frame rate.
Thanks to our friend Eitan, who suggested about making this tutorial to resolve the issue of varying frame rates in the opencv videos. These variations are caused by the fact that, when we display an opencv image in a while loop, we consider it to play from the perspective delay given in the waitKey() function. The delay in waitKey() function is very important to properly render the video at its correct frame rate. So the question is how to keep the inherent frame rate of video while rendering? The probable answer is to stablize the rendering sample time (TS) in the loop, by checking if the current frame rate is higher or lower than the desired inherent frame rate. Accordingly, increment or decrement the sampling time.
The block of code below shows how to obtain the inherent frames per second (FPS) of an MP4 file.
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(filename)
FPS = vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
Let’s say fps is the measured frames per second in real-time, so the code below shows how to regulate the TS:
if fps>FPS:
TS+=0.001
elif fps<FPS:
TS-=0.001
else:
pass
Below is the server.py code, which runs three threads concurrently to obtain the synchronization:
executor.submit(audio_stream) # to generate and send stream of audio data
executor.submit(video_stream_gen) # to generate stream of frames
executor.submit(video_stream) # to obtain and send video stream, with a synchronized fps
Here is the complete server.py code, please follow our previous tutorials about UDP and TCP sockets for more details on finding and running the code properly. Replace the filename = 'count.mp4' with your MP4 file, and also change the host_ip = '192.168.1.21' with yours. At the start, the audio will be extracted from this file and save as ‘temp.wav’. Also note that FFMPEG should be installed in your system path. You may download install FFMPEG from the “Get packages & executable files” section according to your OS. After installing FFMPEG, you can confirm the installation by writing this in terminal:
ffmpeg
and you will see this output like this:
ffmpeg version 3.4.1 Copyright (c) 2000-2017 the FFmpeg developers
built with Apple LLVM version 9.0.0 (clang-900.0.39.2)
...
...
You also need PyAudio, if you can’t install it using pip installer, then please go this link and download the .whl according to your Python version. For instance if you are using Python 3.6 then you need to download this PyAudio‑0.2.11‑cp36‑cp36m‑win_amd64.whl. After that go to the location of this download and open up the power shell or terminal and use the command below:
pip3.6 install PyAudio‑0.2.11‑cp36‑cp36m‑win_amd64.whl
Windows OS
server.py
## This is server code to send video and audio frames over UDP/TCP
import cv2, imutils, socket
import numpy as np
import time
import base64
import threading, wave, pyaudio,pickle,struct
import sys
import queue
import os
## For details visit pyshine.com
q = queue.Queue(maxsize=10)
filename = 'count.mp4'
command = "ffmpeg -i {} -ab 160k -ac 2 -ar 44100 -vn {}".format(filename,'temp.wav')
os.system(command)
BUFF_SIZE = 65536
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET,socket.SO_RCVBUF,BUFF_SIZE)
host_name = socket.gethostname()
host_ip = '192.168.1.21'# socket.gethostbyname(host_name)
print(host_ip)
port = 9688
socket_address = (host_ip,port)
server_socket.bind(socket_address)
print('Listening at:',socket_address)
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(filename)
FPS = vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
global TS
TS = (0.5/FPS)
BREAK=False
print('FPS:',FPS,TS)
totalNoFrames = int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
durationInSeconds = float(totalNoFrames) / float(FPS)
d=vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_MSEC)
print(durationInSeconds,d)
def video_stream_gen():
WIDTH=400
while(vid.isOpened()):
try:
_,frame = vid.read()
frame = imutils.resize(frame,width=WIDTH)
q.put(frame)
except:
os._exit(1)
print('Player closed')
BREAK=True
vid.release()
def video_stream():
global TS
fps,st,frames_to_count,cnt = (0,0,1,0)
cv2.namedWindow('TRANSMITTING VIDEO')
cv2.moveWindow('TRANSMITTING VIDEO', 10,30)
while True:
msg,client_addr = server_socket.recvfrom(BUFF_SIZE)
print('GOT connection from ',client_addr)
WIDTH=400
while(True):
frame = q.get()
encoded,buffer = cv2.imencode('.jpeg',frame,[cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY,80])
message = base64.b64encode(buffer)
server_socket.sendto(message,client_addr)
frame = cv2.putText(frame,'FPS: '+str(round(fps,1)),(10,40),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7,(0,0,255),2)
if cnt == frames_to_count:
try:
fps = (frames_to_count/(time.time()-st))
st=time.time()
cnt=0
if fps>FPS:
TS+=0.001
elif fps<FPS:
TS-=0.001
else:
pass
except:
pass
cnt+=1
cv2.imshow('TRANSMITTING VIDEO', frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(int(1000*TS)) & 0xFF
if key == ord('q'):
os._exit(1)
TS=False
break
def audio_stream():
s = socket.socket()
s.bind((host_ip, (port-1)))
s.listen(5)
CHUNK = 1024
wf = wave.open("temp.wav", 'rb')
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
print('server listening at',(host_ip, (port-1)))
stream = p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(wf.getsampwidth()),
channels=wf.getnchannels(),
rate=wf.getframerate(),
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
client_socket,addr = s.accept()
while True:
if client_socket:
while True:
data = wf.readframes(CHUNK)
a = pickle.dumps(data)
message = struct.pack("Q",len(a))+a
client_socket.sendall(message)
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=3) as executor:
executor.submit(audio_stream)
executor.submit(video_stream_gen)
executor.submit(video_stream)
Usage
python server.py
After running the server.py, a queue of frames will store 10 frames, halt the execution of code and wait for the first frame to be taken out of the queue and then the process of adding and removing frames in queue goes on. Please note that windows of imshow() are placed at predefined locations, if we drag these windows, the operation of displaying frames will affect the synchronization. If the codes are running, please keep the window showing images at their original locations. This is just the proof of concept that video and audio data can be sent from sockets using Python. At any time if you want to quit, click on the image and press q. Below is the client side code. Once the the server is setup, then run the client code below and you will see how the frame rate is stabilizing and keeping the synchronization of audio and video.
client.py
## Welcome to PyShine
## This is client code to receive video and audio frames over UDP/TCP
import cv2, imutils, socket
import numpy as np
import time, os
import base64
import threading, wave, pyaudio,pickle,struct
## For details visit pyshine.com
BUFF_SIZE = 65536
BREAK = False
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
client_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET,socket.SO_RCVBUF,BUFF_SIZE)
host_name = socket.gethostname()
host_ip = '192.168.1.21'# socket.gethostbyname(host_name)
print(host_ip)
port = 9688
message = b'Hello'
client_socket.sendto(message,(host_ip,port))
def video_stream():
cv2.namedWindow('RECEIVING VIDEO')
cv2.moveWindow('RECEIVING VIDEO', 10,360)
fps,st,frames_to_count,cnt = (0,0,20,0)
while True:
packet,_ = client_socket.recvfrom(BUFF_SIZE)
data = base64.b64decode(packet,' /')
npdata = np.fromstring(data,dtype=np.uint8)
frame = cv2.imdecode(npdata,1)
frame = cv2.putText(frame,'FPS: '+str(fps),(10,40),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7,(0,0,255),2)
cv2.imshow("RECEIVING VIDEO",frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if key == ord('q'):
client_socket.close()
os._exit(1)
break
if cnt == frames_to_count:
try:
fps = round(frames_to_count/(time.time()-st))
st=time.time()
cnt=0
except:
pass
cnt+=1
client_socket.close()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def audio_stream():
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
CHUNK = 1024
stream = p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(2),
channels=2,
rate=44100,
output=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
### create socket
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
socket_address = (host_ip,port-1)
print('server listening at',socket_address)
client_socket.connect(socket_address)
print("CLIENT CONNECTED TO",socket_address)
data = b""
payload_size = struct.calcsize("Q")
while True:
try:
while len(data) < payload_size:
packet = client_socket.recv(4*1024) # 4K
if not packet: break
data+=packet
packed_msg_size = data[:payload_size]
data = data[payload_size:]
msg_size = struct.unpack("Q",packed_msg_size)[0]
while len(data) < msg_size:
data += client_socket.recv(4*1024)
frame_data = data[:msg_size]
data = data[msg_size:]
frame = pickle.loads(frame_data)
stream.write(frame)
except:
break
client_socket.close()
print('Audio closed',BREAK)
os._exit(1)
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=2) as executor:
executor.submit(audio_stream)
executor.submit(video_stream)
Usage
python client.py
MAC OS
MAC OS users please increase the size of UDP datagram using below in the terminal:
$sudo sysctl -w net.inet.udp.maxdgram=65535
If the above code does not work for MAC OS users, please use the code below:
server.py
## This is server code to send video and audio frames over UDP/TCP
import cv2, imutils, socket
import numpy as np
import time
import base64
import threading, wave, pyaudio,pickle,struct
import sys
import queue
import os
## For details visit pyshine.com
q = queue.Queue(maxsize=10)
filename = 'av.mp4'
command = "ffmpeg -i {} -ab 160k -ac 2 -ar 44100 -vn {}".format(filename,'temp.wav')
os.system(command)
BUFF_SIZE = 65536
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET,socket.SO_RCVBUF,BUFF_SIZE)
host_name = socket.gethostname()
host_ip = '192.168.1.102'# socket.gethostbyname(host_name)
print(host_ip)
port = 9699
socket_address = (host_ip,port)
server_socket.bind(socket_address)
print('Listening at:',socket_address)
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(filename)
FPS = vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
TS = (1/FPS)
BREAK=False
print('FPS:',FPS,TS)
totalNoFrames = int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
durationInSeconds = float(totalNoFrames) / float(FPS)
d=vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_MSEC)
print(durationInSeconds,d)
def video_stream_gen():
WIDTH=400
while(vid.isOpened()):
try:
_,frame = vid.read()
frame = imutils.resize(frame,width=WIDTH)
q.put(frame)
except:
os._exit(1)
print('Player closed')
BREAK=True
vid.release()
def audio_stream():
s = socket.socket()
s.bind((host_ip, (port-1)))
s.listen(5)
CHUNK = 1024
wf = wave.open("temp.wav", 'rb')
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
print('server listening at',(host_ip, (port-1)))
stream = p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(wf.getsampwidth()),
channels=wf.getnchannels(),
rate=wf.getframerate(),
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
client_socket,addr = s.accept()
while True:
if client_socket:
while True:
data = wf.readframes(CHUNK)
a = pickle.dumps(data)
message = struct.pack("Q",len(a))+a
client_socket.sendall(message)
t1 = threading.Thread(target=audio_stream, args=())
t2 = threading.Thread(target=video_stream_gen, args=())
t1.start()
t2.start()
fps,st,frames_to_count,cnt = (0,0,1,0)
cv2.namedWindow('TRANSMITTING VIDEO')
cv2.moveWindow('TRANSMITTING VIDEO', 10,30)
while True:
msg,client_addr = server_socket.recvfrom(BUFF_SIZE)
print('GOT connection from ',client_addr)
WIDTH=400
while(True):
frame = q.get()
encoded,buffer = cv2.imencode('.jpeg',frame,[cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY,80])
message = base64.b64encode(buffer)
server_socket.sendto(message,client_addr)
frame = cv2.putText(frame,'FPS: '+str(round(fps,1)),(10,40),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7,(0,0,255),2)
if cnt == frames_to_count:
try:
fps = (frames_to_count/(time.time()-st))
st=time.time()
cnt=0
if fps>FPS:
TS+=0.001
elif fps<FPS:
TS-=0.001
else:
pass
except:
pass
cnt+=1
cv2.imshow('TRANSMITTING VIDEO', frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(int(1000*TS)) & 0xFF
if key == ord('q'):
os._exit(1)
TS=False
break
client.py
## Welcome to PyShine
## This is client code to receive video and audio frames over UDP/TCP
import cv2, imutils, socket
import numpy as np
import time, os
import base64
import threading, wave, pyaudio,pickle,struct
## For details visit pyshine.com
BUFF_SIZE = 65536
BREAK = False
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
client_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET,socket.SO_RCVBUF,BUFF_SIZE)
host_name = socket.gethostname()
host_ip = '192.168.1.102'# socket.gethostbyname(host_name)
print(host_ip)
port = 9699
message = b'Hello'
client_socket.sendto(message,(host_ip,port))
def audio_stream():
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
CHUNK = 1024
stream = p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(2),
channels=2,
rate=44100,
output=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
### create socket
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
socket_address = (host_ip,port-1)
print('server listening at',socket_address)
client_socket.connect(socket_address)
print("CLIENT CONNECTED TO",socket_address)
data = b""
payload_size = struct.calcsize("Q")
while True:
try:
while len(data) < payload_size:
packet = client_socket.recv(4*1024) # 4K
if not packet: break
data+=packet
packed_msg_size = data[:payload_size]
data = data[payload_size:]
msg_size = struct.unpack("Q",packed_msg_size)[0]
while len(data) < msg_size:
data += client_socket.recv(4*1024)
frame_data = data[:msg_size]
data = data[msg_size:]
frame = pickle.loads(frame_data)
stream.write(frame)
except:
break
client_socket.close()
print('Audio closed',BREAK)
os._exit(1)
t1 = threading.Thread(target=audio_stream, args=())
t1.start()
cv2.namedWindow('RECEIVING VIDEO')
cv2.moveWindow('RECEIVING VIDEO', 10,360)
fps,st,frames_to_count,cnt = (0,0,20,0)
while True:
packet,_ = client_socket.recvfrom(BUFF_SIZE)
data = base64.b64decode(packet,' /')
npdata = np.fromstring(data,dtype=np.uint8)
frame = cv2.imdecode(npdata,1)
frame = cv2.putText(frame,'FPS: '+str(fps),(10,40),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7,(0,0,255),2)
cv2.imshow("RECEIVING VIDEO",frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if key == ord('q'):
client_socket.close()
os._exit(1)
break
if cnt == frames_to_count:
try:
fps = round(frames_to_count/(time.time()-st),1)
st=time.time()
cnt=0
except:
pass
cnt+=1
client_socket.close()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()