Hello friends! This tutorial is about using raspberry pi to control the focus level of a webcam. Now the question is how to do that? We are using a normal webcam which has manual turning option to adjust is focus level. We can convert this webcam to a useful application to inspect Printed Circuit Boards PCBs or even for chat. To do this we will use the Lego gears to rotate the lense of the webcam. The motor attached to this Lego gears is controlled by Raspberrypi via an interface. The motor can send control signals like Stop, Forward and Back. The next question is how to know when to rotate the lens clockwise, counter-clockwise and when to stop?
To answer this question we will use an image processing algorithm in PC. This algo. will receive the video frames from camera via usb and find the Laplacian variance in video frames. Note that the blur image has less edges and hence less variance so it will be of low focus level. The sharper image has more edges and hence larger value of laplacian variance. The algo. will act as an agent and take the laplacian variance of current frame and the previous frame. The agent will take an initial forward action and check after this action the current variance is higher than previous, if yes then this action will be given a score +=1 otherwise it will be a score of -=1.
The block diagram shows main setup. !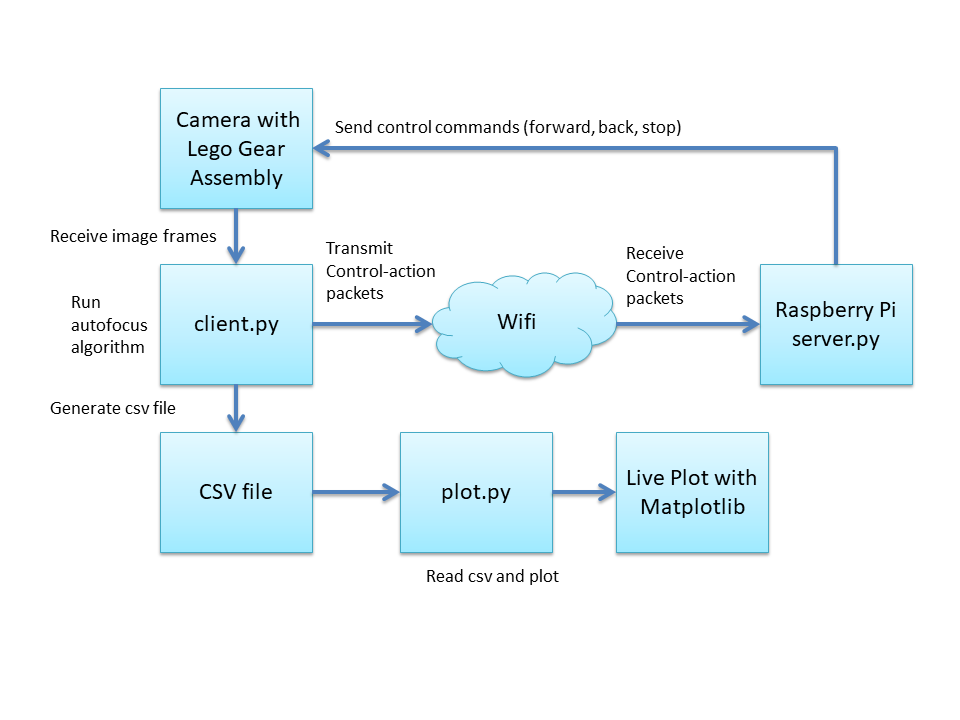
Here is the server.py code that will run on raspberry pi zero w.
server.py
import time
import threading
import socket, pickle, struct
import RPi.GPIO as io
server_ip = '192.168.10.1'
port = 8000
time.sleep(1)
FORWARD = 6
BACK = 27
LEFT = 26
RIGHT = 22
STRAIGHT = 'STRAIGHT'
STOP = 'STOP'
map_motion = {
FORWARD: "FORWARD",
BACK : "BACK",
LEFT : "LEFT",
RIGHT : "RIGHT",
STRAIGHT : 'STRAIGHT',
STOP : 'STOP'
}
my_list =[FORWARD,BACK,LEFT,RIGHT]
def run_for (pin,speed=0):
print(f"action-- {map_motion[pin]}")
if pin != STRAIGHT and pin != STOP:
io.cleanup()
io.setmode(io.BCM)
io.setup(pin, io.OUT)
io.output(pin, True)
io.setup(FORWARD, io.OUT)
io.output(FORWARD, True)
elif pin == STRAIGHT:
io.cleanup()
io.setmode(io.BCM)
io.setup(LEFT, io.OUT)
io.output(LEFT, False)
io.setup(RIGHT, io.OUT)
io.output(RIGHT, False)
io.setup(FORWARD, io.OUT)
io.output(FORWARD, True)
elif pin == STOP:
for x in my_list:
io.setup(x, io.OUT)
io.output(x, False)
def init():
io.setmode(io.BCM)
io.setup(FORWARD,io.OUT)
io.setup(BACK,io.OUT)
io.setup(LEFT,io.OUT)
io.setup(RIGHT,io.OUT)
for x in my_list:
io.output(pin, False)
io.cleanup()
global pin
pin = FORWARD
init()
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
host_name = socket.gethostname()
host_ip = server_ip
print('HOST IP:',host_ip)
port = port+1
socket_address = (host_ip,port)
server_socket.bind(socket_address)
server_socket.listen()
print("Listening at",socket_address)
def show_client(addr,client_socket):
global pin
prev_move = None
frame= 'stop'
try:
print('CLIENT {} CONNECTED!'.format(addr))
if client_socket: # if a client socket exists
data = b""
payload_size = struct.calcsize("Q")
while True:
while len(data) < payload_size:
packet = client_socket.recv(4*1024) # 4K
if not packet: break
data+=packet
packed_msg_size = data[:payload_size]
data = data[payload_size:]
msg_size = struct.unpack("Q",packed_msg_size)[0]
while len(data) < msg_size:
data += client_socket.recv(4*1024)
frame_data = data[:msg_size]
data = data[msg_size:]
frame = pickle.loads(frame_data)
if frame == 'forward':
pin = FORWARD
run_for(pin)
prev_move = pin
elif frame == 'back':
pin = BACK
run_for(pin)
prev_move = pin
elif frame == 'left':
pin = LEFT
run_for(pin)
prev_move = pin
elif frame == 'right':
pin = RIGHT
run_for(pin)
prev_move = pin
elif frame == 'straight':
pin = STRAIGHT
run_for(pin)
prev_move = pin
elif frame == 'stop':
print(frame)
io.setmode(io.BCM)
io.setup(pin, io.OUT)
io.output(pin, False)
io.cleanup()
except Exception as e:
print(f"CLINET {addr} DISCONNECTED")
pass
while True:
client_socket,addr = server_socket.accept()
thread = threading.Thread(target=show_client, args=(addr,client_socket))
thread.start()
print("TOTAL CLIENTS ",threading.activeCount() - 2)
time.sleep(0.1)
Once the server starts listening at its socker address, we can run the client.py on PC.
Here is the client.py code:
# Autofocus application with Python
import cv2, os
import _thread
import socket,pickle,struct
import time
import numpy as np
from collections import deque
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
def cam_run():
server_ip = '192.168.10.1'
port = 8000
queue = deque([],maxlen=7)
i=0
cnt=0
frames_to_count = 40
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
host_ip = server_ip # Here according to your server ip write the address
port = port +1
client_socket.connect((host_ip,port))
msg = 'forward'
forward_done = False
stop_cnt=0
_cx,_cy =50,50
ret, frame = vid.read()
prev_l = 0
print(str(0)+',' +str(0), file=open('file.csv','w'))
score={'forward':50,'back':50}
prev_action='forward'
if client_socket:
while(True):
ret, frame = vid.read()
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
H,W = img_gray.shape
img_gray = img_gray[H//4:(H//2+H//4),W//4:(W//2+W//4) ]
color = (0, 242, 255)
thickness = 1
horizontal_sp = (W//4, H//2)
horizontal_ep = (W//4+20, H//2)
frame = cv2.line(frame, horizontal_sp, horizontal_ep, color, thickness)
horizontal_sp = (W//2+W//4-20, H//2)
horizontal_ep = (W//2+W//4, H//2)
frame = cv2.line(frame, horizontal_sp, horizontal_ep, color, thickness)
vertical_sp = (W//2, H//4)
vertical_ep = (W//2, H//4+20)
frame = cv2.line(frame, vertical_sp, vertical_ep, color, thickness)
vertical_sp = (W//2, H//2+H//4-20)
vertical_ep = (W//2, H//2+H//4)
frame = cv2.line(frame, vertical_sp, vertical_ep, color, thickness)
start_point = (W//4, H//4)
end_point = (W//4 +W//2 ,H//4 +H//2 )
frame = cv2.rectangle(frame, start_point, end_point, color, thickness)
laplacian_var = round(cv2.Laplacian(img_gray, cv2.CV_64F).var(),4)
cv2.putText(frame, 'Focus level: '+str(int(laplacian_var)), (20, 40), fontFace=1, fontScale=2, color=color, thickness=2)
queue.append(laplacian_var)
cv2.imshow('PyShine AutoFocus', frame)
if cnt == frames_to_count//4:
score={'forward':50,'back':50}
if cnt == frames_to_count:
laplacian_var = np.median(queue)
if laplacian_var>prev_l:
score[prev_action]+=1
else:
score[prev_action]-=1
if score['forward']>score['back']:
msg ='forward'
else:
msg = 'back'
prev_action = msg
if laplacian_var>500 or laplacian_var < 1:
msg = 'stop'
a = pickle.dumps(msg)
message = struct.pack("Q",len(a))+a
client_socket.sendall(message)
cnt=0
print(str(i)+',' +str(laplacian_var), file=open('file.csv','a'))
prev_l = laplacian_var
print(laplacian_var,msg, score)
if i==3000:
print(str(i)+',' +str(laplacian_var), file=open('file.csv','w'))
i=0
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
i+=1
cnt+=1
def plot():
os.system('python plot.py')
_thread.start_new_thread(plot,())
cam_run()
vid.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
The client code will also call the plot.py code, to read and plot the csv in real-time. Please note that set the proper version of python or python3 here os.system('python plot.py').
Just keep the plot.py in the same PC and same directory as client.py code.
Here is the plot.py code.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.set_facecolor((0,0,0))
def animate(i):
ax.clear()
xs = []
ys = []
graph_data = open('file.csv','r').read()
lines = graph_data.split('\n')
for line in lines[1:]:
if len(line) > 1:
x, y = line.split(',')
xs.append(float(x))
ys.append(float(y))
ax.clear()
ax.plot(xs, ys,'-o', color = (0,1,0.25))
ax.set_ylim( ymin=0, ymax=1800)
ax.set_xlabel("Samples")
ax.set_ylabel("")
ax.set_title("Auto Focus")
fig.tight_layout() # To remove outside borders
ax.yaxis.grid(True)
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, interval=100)
plt.show()