Today i am going to start a tutorial series about Keras library. Lets visit website of this Deep learning library https://keras.io. Keras is a high-level neural networks API. What is API? Its Application Program Interface. API is a set of routines, protocols, and tools for building software applications. It is written in Python and its open source. We can have a deeper look into different learning networks. It is built on top of different libraries such as TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.
What is a Tensor and its flow
The term Tensor is used for an N dimensional array, where N can be any number and in Neural Networks we have layers as shown here: input -> first hidden layer-> second hidden layer->…output. So tensors flow from input to these layers from one layer to another thats why it is called tensor flow. Just like we pass a matrix to one layer and it is multiplied by weights and then passed to another.
Keras simple Sequential Model
Simplest type of model is the Sequential() model. Lets make a new folder named lab1 and make an empty python file named basic.py. First we need to import an empty Sequential model. Add this code to basic.py.
from keras.models import Sequential
Since this is a very basic tutorial, lets save this model and view it. We need to import plot_model that can help us to save the image of model.
from keras.utils import plot_model
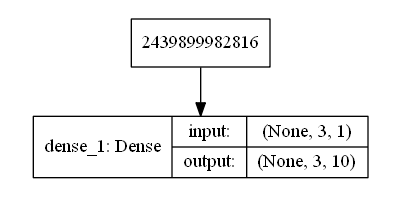
Lets import input layer (Dense) and add it to the empty Model. The Dense layer’s input_shape is (3,1). It can be fed with a matrix of 3 columns and 1 dimension. The number of rows of the input matrix can be of any length. By default the input_shape has a None for the number of rows in the input matrix. The input matrix is used for the X_train or X_test part of the data. On the other hand Y_train or Y_test are the output of the Dense layer. The 10 which is first element in the Dense layer, defines the number of output units.
from keras.layers import Dense
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(10,input_shape=(3, 1), activation='sigmoid'))
This simple Dense layer model will take an input data with shape of (Any-number-of-rows,3 columns,1 dimension). The output will be a vector of size 10. Lets see how our model looks like by adding this last line to the code. And lets run the code. Open powershell and type : python basic.py. As a result you will find a mymodel.png file in the lab1 folder.
plot_model(model, to_file='mymodel.png', show_shapes=True)
Thats all for this lab 1. In the next lab 2 we will learn about more layers to a model. Thanks for reading. Code is available. I hope this will be helpful for the beginners.